PHP $_GET & $_POST Variables
PHP $_GET & $_POST are part of PHP global variables, and can be called anywhere in PHP scripts, both $_GET & $_POST captures data sent with HTML post and get methods. Example below shows how we can use $_GET and $_POST with HTML form to collect data.Collecting data from HTML Form
The HTML page below contains HTML form with input elements like text fields, checkboxes, radio-buttons, submit buttons. When user fills these elements and clicks submit button, the data is sent to "grab_values.php", which is specified in action form element.Picture below illustrates a typical HTML form procedure with GET method. Next picture is the result of form data captured by PHP page.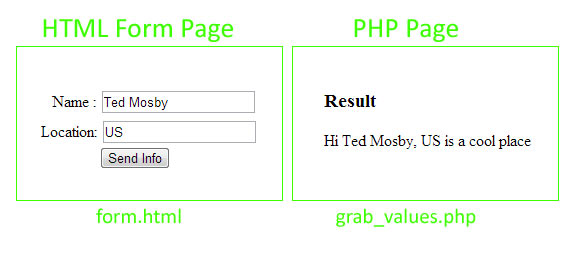 .
.HTML GET Method
Have a look at HTML form code below. In the form element, we need to specify how we are going to send data to server in "method" form element.HTML
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
<form action="grab_values.php" method="GET">
User Name: <input type="text" name="user_name" />
Location: <input type="text" name="user_location" />
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>PHP
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
<?php
echo 'Hi '.$_GET["user_name"];
echo $_GET["user_location"].' is a cool place';
?>- GET requests can be cached
- GET requests remain in the browser history
- GET requests can be bookmarked
- GET requests should never be used when dealing with sensitive data
- GET requests have length restrictions
- GET requests should be used only to retrieve data
HTML POST Method
A large sized post request can be sent using POST method, since HTML 4.0, forms can also submit data in multipart/form-data as defined in RFC 2388. POST method works similar way as GET, but it is safer than GET because the values are not visible on the address bar and will not be stored in browser history.To use POST just change element method to POST as shown below :HTML
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
<form action="grab_values.php" method="POST">
User Name: <input type="text" name="user_name" />
Location: <input type="text" name="user_location" />
<input type="submit" value="Send My Info">
</form>PHP
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
<?php
echo 'Hi '.$_POST["user_name"];
echo $_POST["user_location"].' is a cool place';
?>- POST requests are never cached
- POST requests do not remain in the browser history
- POST requests cannot be bookmarked
- POST requests have no restrictions on data length
Error Handling
We should always be careful while collecting GET/POST data, because if a user enters empty values, above PHP script will end-up with an error message on the screen, to deal with unnecessary errors we can use PHP variable handling Functions, something like isset(). This function will return TRUE if the variable exist, allowing us to display a friendly message instead of nasty error. let's modify grab_values.php so it can deal gracefully with empty variables.PHP
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
<?php
//!(exclamation mark) returns the opposite value of the boolean variable,
//it means isset() will return true if value is empty.
if(!isset($_POST["user_name"])) //isset returns true when value is empty
{
die("Please go back and enter name"); //exit page after outputting the message.
}
if(!isset($_POST["user_location"]))
{
die("Please go back and enter Location"); //exit page after outputting the message.
}
//output result
echo 'Hi '.$_POST["user_name"];
echo $_POST["user_location"].' is a cool place';
?>